

The secreted insulin is then carried through the circulation to peripheral tissues, where insulin receptor activation stimulates glucose uptake and utilization and/or storage as glycogen, reducing blood glucose ( Bjornholm and Zierath, 2005 DeFronzo et al., 1985). The resulting depolarization of the plasma membrane then provokes influx of extracellular Ca 2+, activation of insulin-containing vesicle exocytosis and thus secretion of insulin ( Deeney et al., 2000 Rutter, 2001). Typically, following postprandial hyperglycemia, the glucose metabolism in beta cells induces an increase in the ATP/ADP ratio, which triggers closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K ATP). This crystalline structure is osmotically stable at pH 5.5 until secretion ( Dodson and Steiner, 1998 Emdin et al., 1980). Insulin is stored inside pancreatic beta cell secretory vesicles, in which six insulin molecules form solid hexamers with two Zn 2+ ions. muscle and fat cells, and inhibiting hepatic glucose production ( DeFronzo et al., 1992). Insulin, a pancreatic hormone produced by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans, tightly regulates glucose homeostasis by promoting glucose uptake from plasma by peripheral tissues, i.e.
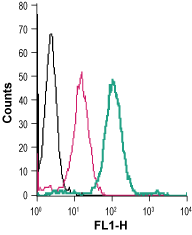
Altogether, these data strongly suggest that the zinc transporter ZnT-8 is a key protein for both zinc accumulation and regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells. Furthermore, ZnT-8-overexpressing cells display enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion compared with control cells, only for a high glucose challenge, i.e. ZnT-8 overexpression stimulated zinc accumulation and increased total intracellular zinc in insulin-secreting INS-1E cells. In human pancreatic islet cells, ZnT-8 was exclusively expressed in insulin-producing beta cells, and colocalized with insulin in these cells. In this paper we studied its localization in human pancreatic islet cells, and its effect on cellular zinc content and insulin secretion. We previously identified a pancreas-specific zinc transporter, ZnT-8, which colocalized with insulin in cultured beta cells. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying zinc accumulation in insulin-containing vesicles. Secreted zinc has also been proposed to be a paracrine and autocrine modulator of glucagon and insulin secretion in pancreatic alpha and beta cells, respectively. In these cells, zinc is required for zinc-insulin crystallization within secretory vesicles. Insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cells are exceptionally rich in zinc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
